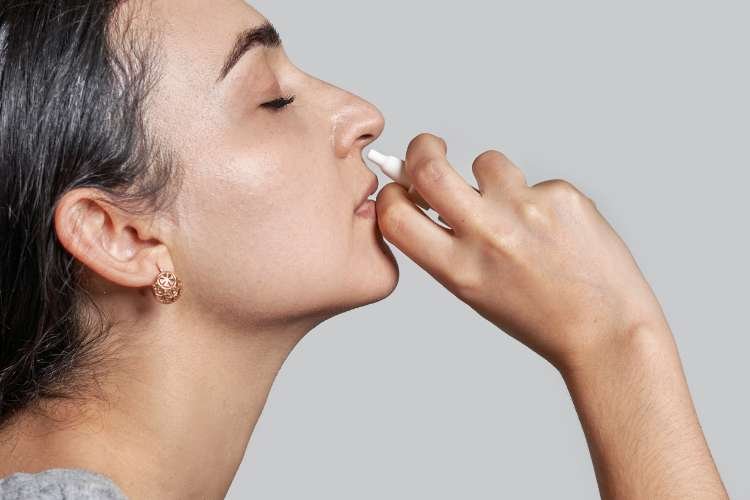
Pneumagen, the Scottish pharmaceutical company, has achieved a significant breakthrough in the fight against influenza through an unconventional approach to a human challenge study. Their intranasal flu antiviral, Neumifil, demonstrated its effectiveness in reducing both the rate of symptomatic infection and the severity of viral respiratory tract infections during a phase 2 proof-of-concept trial.
In this unique study, 104 healthy adults volunteered to intentionally contract an influenza infection and were meticulously monitored throughout the process. Prior to exposure to the influenza virus, these individuals received two doses of Neumifil.
The results of the trial were nothing short of remarkable. Neumifil displayed a clinically substantial reduction in the occurrence of symptomatic flu infection and a decrease in symptom severity, successfully achieving the primary objective of the study. Furthermore, Neumifil exhibited an excellent safety profile, with no notable treatment-related adverse events or safety concerns when compared to an earlier phase 1 study.
Also Read: CDC Launches ‘Wild To Mild’ Campaign To Boost Flu Vaccination Rates Among High-Risk Groups
Armed with this promising proof of concept, Pneumagen is now poised to advance into further clinical trials for Neumifil. Among their future endeavors is a phase 2b trial slated to commence in 2024, with the aim of investigating Neumifil’s potential to mitigate viral exacerbations in patients afflicted with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
Also Read: Influenza Variant Virus In Brazil: What You Need To Know
Neumifil stands as the flagship therapy for Pneumagen, a company that originated from the University of St Andrews in Scotland and is now headquartered in St. Andrews, UK In a testament to the significance of their achievement, Pneumagen secured an impressive £8 million ($9.6 million) in financing in June to bolster their clinical development program. This breakthrough not only marks a significant stride forward in the fight against influenza but also underscores the potential of innovative approaches to tackle infectious diseases, offering hope to countless individuals worldwide.