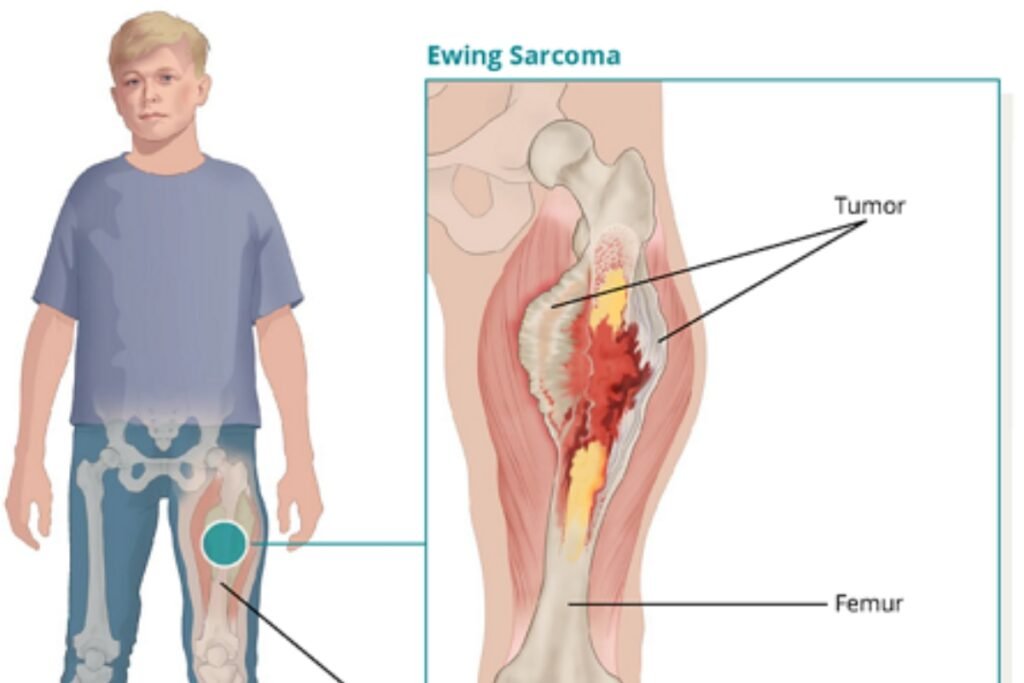
Ewing Sarcoma Cancer is a rare form of cancer that primarily affects the bones or the soft tissues surrounding them. Although it is most commonly diagnosed in children and young adults, it can occur at any age. Symptoms of Ewing sarcoma include pain, swelling, and occasionally fever or weight loss. The cancer has the potential to spread to other parts of the body, such as the lungs, liver, or bone marrow.
Treatment of Ewing sarcoma Cancer depends on several factors, including the size and location of the tumor, the stage of the disease, and the patient’s age and overall health. The treatment of Ewing sarcoma mainly involves a combination of surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy. Chemotherapy is usually administered first to shrink the tumor, followed by surgery to remove the tumor if possible, radiation therapy may be used before or after surgery to target any remaining cancer cells.
Ewing Sarcoma Cancer Treatments
Ewing Sarcoma Cancer Treatments: It involves the removal of the tumor along with some surrounding healthy tissue. The primary objective of surgery is to eliminate as much of the cancer as possible while preserving the function and appearance of the affected body part. However, there are instances when surgery alone is insufficient to eradicate all traces of the cancer. In such cases, chemotherapy and/or radiation therapy may be administered before or after surgery to shrink the tumor or eliminate any remaining cancer cells.
Chemotherapy in Treatment of Ewing Sarcoma Cancer
It utilizes drugs to destroy or inhibit the growth of cancer cells. These drugs are typically administered intravenously or through a port, which is a device implanted under the skin to facilitate vein access. Chemotherapy is administered in cycles, alternating between treatment periods and resting periods. The duration and number of cycles depend on the specific drugs used, their dosages, and the patient’s ability to tolerate them. Side effects of chemotherapy may include hair loss, nausea, vomiting, fatigue, susceptibility to infections, and low blood cell counts. The most common chemotherapy combination used to treat Ewing Sarcoma Cancer in the United States is vincristine, doxorubicin, and cyclophosphamide, alternating with ifosfamide and etoposide. Chemotherapy is typically the first treatment of ewing sarcoma given to almost all patients with Ewing sarcoma.
In addition to the standard chemotherapy regimen, other chemotherapy combinations such as vincristine/irinotecan/temozolomide or gemcitabine/docetaxel have been considered in recurrent Ewing sarcoma. A randomized study comparing the vincristine, doxorubicin, cyclophosphamide, and actinomycin C regimen with the vincristine, doxorubicin, and ifosfamide regimen showed no significant difference in overall survival or event-free survival
Radiation therapy For Ewing Sarcoma
Radiation therapy in treatment of Ewing Sarcoma involves the use of high-energy rays or particles to destroy cancer cells or prevent their growth. It can be delivered externally from a machine outside the body or internally through the placement of radioactive materials near the tumor. Radiation therapy is typically administered in small doses over several weeks. Side effects may include skin irritation, hair loss, fatigue, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and mouth sores.
Treatment of relapsed or refractory Ewing Sarcoma
Standardized second-line treatment plans for relapsed or refractory Ewing Sarcoma Cancer are currently lacking. The vincristine, doxorubicin (Adriamycin), and cyclophosphamide/ ifosfamide and etoposide (VDC/IE) regimen has been successful in improving survival rates, but patients with metastatic Ewing sarcoma continue to face unfavorable outcomes, leading to an increased demand for new therapeutic options. While targeted treatments, immunotherapies, precision oncology, and other innovative approaches are being utilized to treat various types of cancer, chemotherapy remains the primary treatment for many sarcoma subtypes. Unfortunately, there is a scarcity of approved drugs for effectively treating several sarcoma subtypes, particularly in cases of disease progression.
The treatment of Ewing Sarcoma Cancer presents challenges and can impact a patient’s physical and emotional well-being. Therefore, it is crucial to have a team of healthcare professionals providing medical care, support, and guidance throughout the treatment journey. This multidisciplinary team may include oncologists, surgeons, radiologists, radiation oncologists, pathologists, nurses, social workers, psychologists, nutritionists, physical therapists, and others.
In the latest version (2.2023) of the NCCN guidelines, an update has been made to include lurbinectedin as a second-line therapy option for Ewing sarcoma in cases of relapsed or metastatic disease. This addition is categorized as 2B, indicating its usefulness in specific circumstances as a recommendation.
The prognosis for patients with Ewing sarcoma depends on various factors, such as the stage of the disease, response to treatment, and the patient’s age and overall health. The survival rate for patients with localized Ewing sarcoma (limited to the bone or nearby tissues) is approximately 70% to 80%. For patients with metastatic Ewing sarcoma (spread to other parts of the body), the survival rate is about 30% to 40%. It is important to note that these figures are averages and individual outcomes may vary. Some patients may experience more favorable or unfavorable results.
Ewing sarcoma is a serious condition that necessitates prompt diagnosis and treatment. Nevertheless, advancements in medical research and technology have provided more treatment options and increased hope for patients with this disease. By collaborating with their healthcare team and receiving support from loved ones, individuals with Ewing sarcoma can effectively cope with the challenges they face and lead fulfilling lives.
Emerging players for the Treatment of Ewing Sarcoma
Prominent pharmaceutical companies such as Salarius Pharmaceuticals (Seclidemstat), Jazz Pharmaceuticals (Lurbinectedin), Pfizer (Palbociclib), Eli Lilly and Company (Abemaciclib), BioAlta (Mecobtamab vedotin), Inhibrx (INBRX-109), and others are primarily engaged in the development of therapies for Ewing Sarcoma Cancer. The relatively small number of players in this field can be attributed to the limited patient population affected by Ewing sarcoma. These major companies specifically concentrate on the development of treatments for patients who have reached the second line (2L) of treatment. The critical shortage of effective treatment options for Ewing sarcoma highlights the pressing need for advancements in addressing this disease.